

The formation of sodium chloride from the elemental states at 25∘C and 1 atm can be described as Let’s calculate lattice enthalpy for sodium chloride So, if we know two values of enthalpy changes for the three separate reactions shown on this diagram (the three black arrows), we can easily calculate the third. The enthalpy change for A would be the sum of all energies involved for steps B1 and B2. We can draw this diagrammatically asįor Hess's cycle, the overall enthalpy change in these two routes will be the same. Born & Haber both applied this law in determining lattice enthalpy. Read more about Lattice Enthalpy Calculate lattice enthalpy using Born-Haber Cycleīonr-Haber cycle is an application of Hess’s cycle which states that the enthalpy change in a chemical change is independent of path by which the chemical change is taking place. We can calculate lattice enthalpy by Born-Haber Cycle. However, it is impossible to measure the lattice enthalpy of solid as we cannot form solid from gaseous ions in practice. We can define whether the bonding is purely ionic or not. It describes the nature of bonding in a solid crystalline compound. Lattice enthalpy explains many practical properties of ionic compounds including solubility, hardness, and volatility. For example in the case of sodium chloride, we can write it down as: What does lattice enthalpy tell us?

In both ways, the net amount of energy change would be the same, but with different signs. In other words, it is energy acquired when one mole of solid is broken up to make its constituent gaseous ions. It can be defined as the energy released when two gaseous ions are combined together to form one mole of a solid at 0K. Higher the lattice enthalpy value, the stronger the ionic forces. The strength of this ionic bond is given by lattice enthalpy. These ions arrange themselves in a structured pattern called lattice or ionic crystal. The resulting two ions (Na + and Cl -) get into a columbic interaction (attraction between two opposite charges) and hence associate themselves in a chemical bond called an ionic bond. Here chlorine prefers to acquire one electron to complete its outmost shell and in the process, it gains a unit negative charge forming a chloride ion (Cl -). In the case of chlorine, its electronic configuration is Similarly, atoms that tend to acquire electron gain unit negative charge and the energy released in acquiring an extra electron is called electron affinity. Sodium loses one electron and in this process, it acquires a unit positive charge. In a typical example of sodium, its electronic configuration is: The energy required to remove one electron from the valance shell of an atom in its gaseous state is called its first ionization energy. Atoms that tend to lose electrons thus get a positive charge.
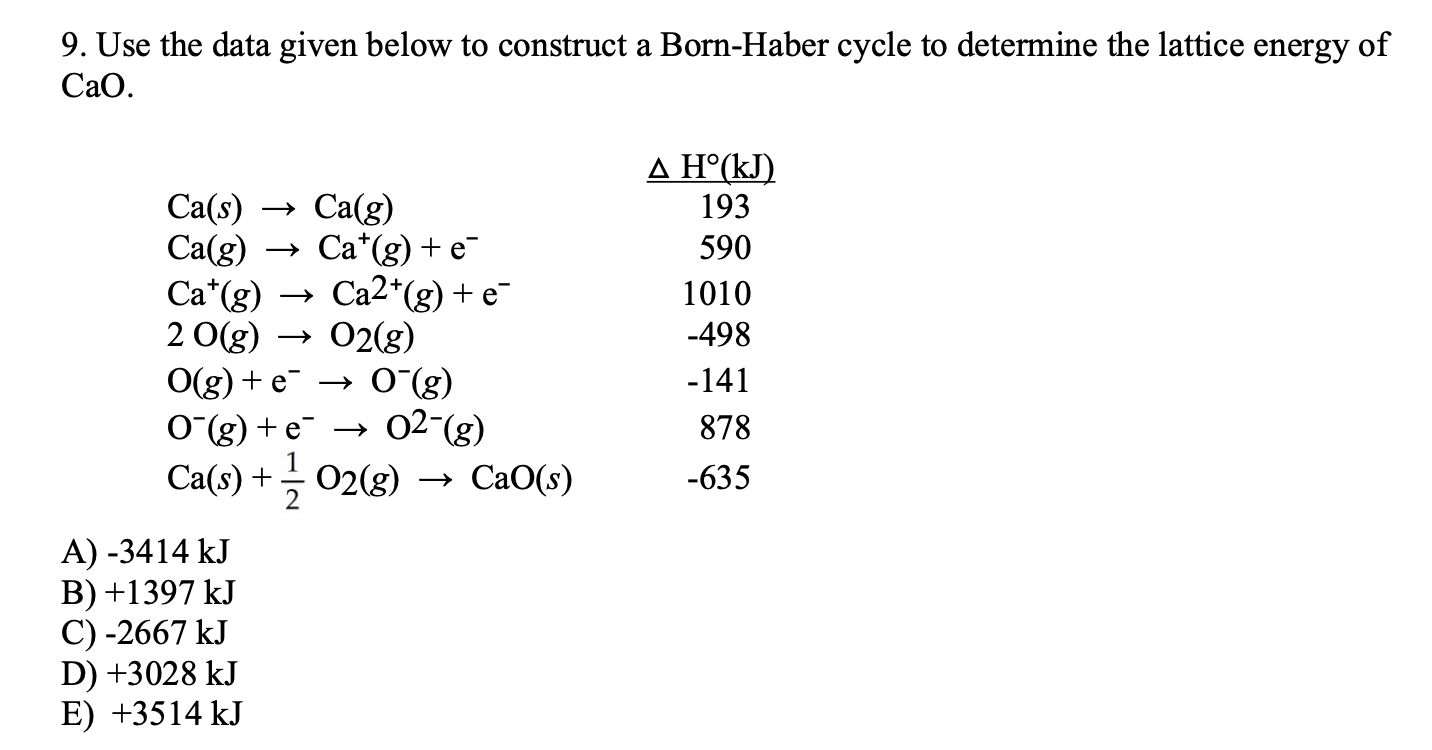
Calculate lattice enthalpy using Born-Haber Cycle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
